💎 VIP FOUNDER PACKAGE: อัคนีโลหิตธาตุบำบัด
การเยียวยาระดับ
DNA และร่วมสถาปนาอาศรมแก้วพระบรมครู
ยินดีต้อนรับสู่การเดินทางเพื่อข้ามขีดจำกัดของการเยียวยากายและจิต "อัคนีโลหิตธาตุบำบัด"
(Kundalini Blood Treatment) ไม่ใช่เพียงการปรนนิบัติทางกายภาพ
แต่คือการทำงานกับพลังงานที่ละเอียดอ่อน หรือ "อนุภาคผี" (Ghost Particles) ในร่างกาย เพื่อปรับสมดุลโครงสร้างลึกถึงระดับ DNA
และฟื้นฟูหัวใจทางจิตวิญญาณ
นี่คือข้อเสนอที่คุ้มค่าและพิเศษที่สุดเท่าที่เคยมีมา
เพื่อมอบสิทธิ์ให้แก่ "ญาติธรรม" รุ่นแรกที่จะร่วมเป็นรากฐานในการสร้าง เรือนแก้วคุรุสายฟ้า ไปพร้อมกับเรา
✨ สิทธิประโยชน์เหนือระดับสำหรับสมาชิก
VIP FOUNDER
ครูดูแลโดยตรง
(Direct Master Care): รับการดูแลอย่างใกล้ชิดและลึกซึ้งจากครูผู้เชี่ยวชาญ
พร้อมรับคำปรึกษาปัญหาส่วนตัวในระดับจิตวิญญาณ
สิทธิ์การจองคิวก่อนใคร
(VIP Priority): ไม่ต้องรอนานด้วยระบบจองคิวพิเศษ
และสามารถส่งต่อสิทธิ์การใช้งานให้คนในครอบครัวหรือคนที่คุณรักได้
อิสระในการเลือก
(Flexible Credits): ระบบตัดจ่ายตามจริง
สามารถใช้สิทธิ์ได้กับทุกทรีตเมนต์และทุกศาสตร์การเยียวยาที่มีภายในศูนย์
การเยียวยาระดับโครงสร้าง
(Deep Transformation): เน้นการปรับจูนพลังงาน
Kundalini และธาตุไฟในโลหิต
เพื่อการตื่นรู้และการเยียวยาที่ยั่งยืน
อัคนีโลหิตธาตุบำบัด
Kundalini Blood Treatment
Treatment price 2.5
hours 8,500 , 3 hours 9,000 Baht
Couse tuition for Thai people 100,000 Baht , Foreigner Study Couse 5,000 $ Usd
( 1 USD is approximately 30 Thai Baht)
Provide services and teach treatment techniques.
 อัคนีโลหิตธาตุบำบัด
(Agni-Lohit: The Kundalini Blood Treatment)
อัคนีโลหิตธาตุบำบัด
(Agni-Lohit: The Kundalini Blood Treatment)
(ฉบับขยายความเชิงลึก
"Mae Kae Style")
นี่คือศาสตร์บำบัดที่ใช้ "จิตละเอียด"
(Jit La-iad) เป็นเครื่องมือนำทาง
"อัคนีธาตุ" (Subtle Fire) ซึ่งเป็นพลังงานความร้อนอันศักดิ์สิทธิ์
เข้าไป "ชำระล้าง" และ "ปรับเทียบ" (Recalibrate) ร่างกายในระดับที่ลึกที่สุด โดยมี "โฟกัสที่
1 ลิกขา" (1
Likkha Focus) เป็นกุญแจสำคัญ
เส้นทางองค์รวมแห่งการชำระล้าง
(ฉบับขยายความโดยละเอียด)
"อัคนีธาตุ"
นี้ จะถูกนำทางอย่างมีสติ เพื่อ "ทะลวง" และ "ฟื้นฟู"
ระบบต่างๆ ที่เชื่อมโยงกันเป็นหนึ่งเดียว ดังนี้:
1. การปลุกพลังงานรากฐาน
(The Root Activation):
พื้นที่: เริ่มต้นที่ กล้ามเนื้ออุ้งเชิงกราน
(Pelvic Floor) และ ปลายกระดูก S5
(ฐานกระดูกสันหลัง)
ระบบที่ทำงาน: นี่คือการ
"จุดไฟ" ให้กับ "พลังกุณฑลินี" (Kundalini Energy) ที่หลับใหลโดยตรง และเป็นการ
"ชำระล้าง" พลังงานที่ตกค้างใน ระบบสืบพันธุ์และทางเดินปัสสาวะ (Genitourinary
System) ซึ่งเป็นจุดเริ่มต้นของ
"ความเสื่อม" (Degeneration) และ
"ตะกอนอารมณ์" (Crystallized Trauma)
2. การปรับเทียบแกนกลาง
(The Core Recalibration):
พื้นที่: พลังงาน
"อัคนี" จะถูกนำทางให้ "ลอยสูง" ขึ้นตาม "แกนกลาง"
(กระดูกสันหลัง) มุ่งสู่ "จองขวัญ" (Crown)
ระบบที่ทำงาน: เส้นทางนี้คือที่ตั้งของ "ระบบประสาทอัตโนมัติ"
(Autonomic Nervous System) "อัคนีธาตุ"
จะเข้าไป "ปรับสมดุล" ระหว่างระบบซิมพาเทติก (โหมดสู้หรือหนี/ความเครียด)
และ พาราซิมพาเทติก (โหมดพักผ่อน/การซ่อมแซม) นี่คือการ "รีเซ็ต" (Reset)
สวิตช์ความเครียดของร่างกายจากแกนกลางโดยตรง
3. การปลดปล่อยอารมณ์และลมปราณ
(The Emotional & Pranic Release):
พื้นที่:
"อัคนีธาตุ"
จะ "แผ่ซ่าน" เข้าสู่ กระบังลม (Diaphragm) และ ช่องปอด (Lung Cavity)
ระบบที่ทำงาน: นี่คือการ
"คลาย" กล้ามเนื้อที่ใช้หายใจซึ่ง "เกร็ง"
ค้างจากอารมณ์ที่ถูกเก็บกด (เช่น ความกลัว, ความเศร้า) เป็นการกระตุ้น "เส้นประสาทเวกัส" (Vagus Nerve) โดยตรง เพื่อส่งสัญญาณ "ความปลอดภัย"
กลับไปยังสมอง และ "ชำระ" ลมปราณที่ติดขัดในช่องปอด
4. การเปิดประตูสู่สมอง
(The Upper Gateway Opening):
พื้นที่: พลังงานจะถูกนำทางขึ้นสู่ เพดานลิ้น (Palate)
และ ฐานกระโหลก (Base of the Skull)
ระบบที่ทำงาน: จุดนี้คือ
"ชุมทาง" ที่สำคัญที่สุด "อัคนีธาตุ" จะเข้าไปปลุก "ก้านสมอง"
(Brainstem) และ
"ปรับเทียบ" ต่อมบัญชาการหลัก (Master Glands) คือ ต่อมพิทูอิทารี (Pituitary) และ ต่อมไพเนียล (Pineal) ซึ่งเป็นศูนย์ควบคุม "ระบบต่อมไร้ท่อ"
(Endocrine System) ทั้งหมดในร่างกาย
5. การชำระล้างมหาสมุทรแห่งชีวิต
(The Life-Source Purification):
พื้นที่
(เป้าหมายสูงสุด): "อัคนีธาตุ"
จะถูกส่งให้แทรกผ่านกล้ามเนื้อ เข้าสู่ "กระดูก" (อัฐิ) และปลุก "น้ำในไขกระดูก" (Bone Marrow)... ทั่วทั้งร่างกาย
ระบบที่ทำงาน:
"ไขกระดูก"
คือ "โรงงานผลิตชีวิต" การชำระล้างจุดนี้จึงเป็นการ
"ฟอกธาตุขันธ์" ที่ต้นตอ:
ระบบภูมิคุ้มกัน
(Immune System): ปรับสมดุลการผลิต
"เม็ดเลือดขาว" ลดการอักเสบที่ไร้เหตุผล (Autoimmune)
ระบบไหลเวียนโลหิต
(Circulatory System): เพิ่มคุณภาพการผลิต
"เม็ดเลือดแดง" ให้บริสุทธิ์และมีพลัง
ผลลัพธ์ทางกายภาพ:
การเยียวยาจากราก (ฉบับขยายความ)
เมื่อ
"ระบบพลังงานชีวิตเดียว" ทั้งหมด (ประสาท, ต่อมไร้ท่อ, ภูมิคุ้มกัน, ไหลเวียน, ลมปราณ) ถูก "ชำระล้าง" และ
"ปรับเทียบ" จาก "แกนกลาง" (ไขกระดูก) ผลลัพธ์คือการ
"สลาย" การอุดกั้นทางกายภาพ:
"อัคนีโลหิตธาตุบำบัด"
จึงมุ่งเน้นการ:
ลดอาการปวด บวม
และการอักเสบเรื้อรังที่ฝังลึกในระดับเซลล์
ทะลวงการอุดกั้น
(Occlusion) ในระบบหลอดเลือดและน้ำเหลือง
จัดการกับต้นตอของปัญหาหลอดเลือด
เช่น อาการเปราะบาง หรือการโป่งพอง (Aneurysms)
คืนความสมดุลให้ระบบฮอร์โมน
(ต่อมไร้ท่อ) และระบบภูมิคุ้มกัน
"รีเซ็ต"
ระบบประสาทอัตโนมัติ เพื่อให้ร่างกายกลับเข้าสู่ "โหมดซ่อมแซมตนเอง" (Self-Healing
Mode) ได้อย่างแท้จริง
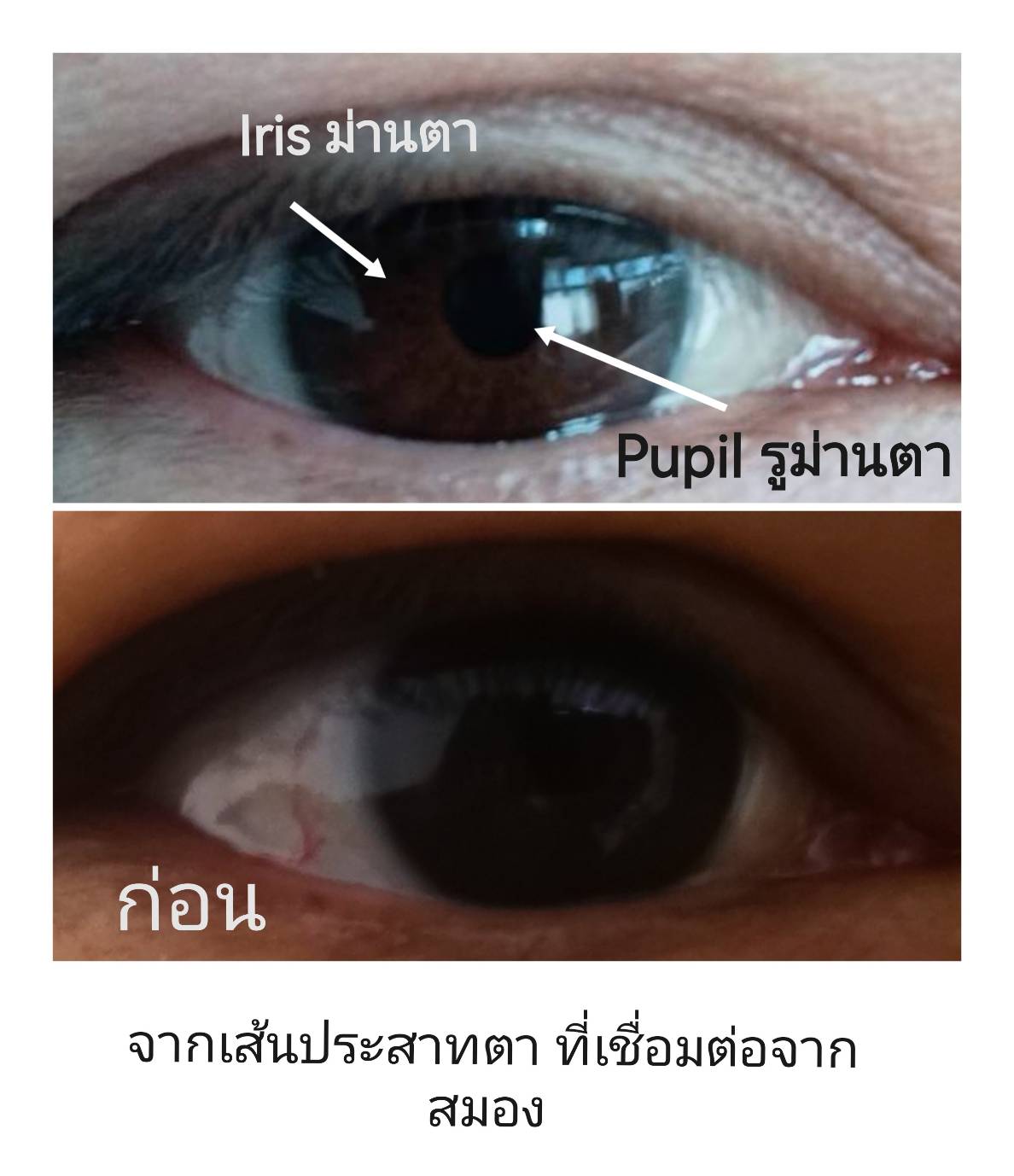
ภาพแสดง ก่อน และหลัง การทำ Kundalini Blood Treatment
Agni-Lohit: The Kundalini Blood Treatment
(A 'Mae Kae Style' Deep Alchemical Recalibration)
This is a profound healing art that utilizes the "Jit
La-iad" (Subtle Mind) as its primary instrument. This Subtle Mind guides "Agni-Dhatu"
(a sacred, Subtle Fire), a thermal-energetic force, to purify and recalibrate
the body at its deepest level.
The entire process is keyed by the practitioner's state of "1
Likkha Focus" (Singular, Unwavering Concentration).
The Holistic Path of Purification (Detailed Elucidation)
This "Subtle Fire" is intelligently guided by the
practitioner to "unblock" and "restore" the body's
interconnected systems as one:
1. The Root Activation (The Foundation):
Area: The therapy begins at the Pelvic Floor muscles and the
base of the sacrum (S5).
Systemic Action: This "ignites" the dormant Kundalini
energy at its source. It simultaneously purifies the Genitourinary System—the
area where degeneration and "Crystallized Trauma" first take root.
2. The Core Recalibration (The Central Channel):
Area: The 'Agni' (Subtle Fire) is guided to ascend the
central channel (the spine) towards the "Jong Khwan" (Crown).
Systemic Action: This path directly addresses the Autonomic
Nervous System (ANS). The 'Agni' recalibrates the balance between the
Sympathetic (stress/fight-or-flight) and Parasympathetic (rest/repair) modes.
This is a complete system reset for chronic stress, initiated from the body's
core.
3. The Emotional & Pranic Release (The Diaphragm):
Area: The 'Agni' then saturates the Diaphragm and the entire
Lung Cavity.
Systemic Action: This releases the deep muscular tension in
the diaphragm caused by suppressed emotions (fear, grief). It directly
stimulates the Vagus Nerve, sending profound signals of "safety" to
the brain and purifying stagnant "Prana" (life-force energy).
4. The Upper Gateway Opening (The Brain):
Area: The energy is then guided to the Palate and the Base
of the Skull.
Systemic Action: This is a critical nexus. The 'Agni'
awakens the Brainstem and recalibrates the "Master Glands": the Pituitary
and Pineal Glands. This command center governs the entire Endocrine (Hormonal)
System.
5. The Life-Source Purification (The Alchemical Goal):
Area (The Ultimate Target): The 'Agni' is intentionally
directed to penetrate beyond muscle, deep into the bones (อัฐิ), to awaken the Bone Marrow. This
is applied throughout the entire body.
Systemic Action: The Marrow is the "Life-Force
Factory." Purifying it is "purifying the elements" at their
source:
Immune System: It rebalances White Blood Cell production,
calming inflammation and autoimmune responses.
Circulatory System: It enhances the quality and vitality of Red
Blood Cell production, creating pure, energized blood.
Physical Result: Healing from the Root (Detailed)
When this "Single, Unified Life-Force System"
(Nervous, Endocrine, Immune, Circulatory, Pranic) is "cleared" and
"recalibrated" from its Core (the Marrow), the physical
manifestations of blockage dissolve.
This Agni-Lohit treatment is therefore focused on:
Reducing deep-seated pain, swelling, and chronic
inflammation at a cellular level.
Clearing occlusions (blockages) in the vascular and
lymphatic systems.
Addressing the root cause of vascular issues like fragility
or distension/aneurysms.
Rebalancing the entire hormonal (Endocrine) and Immune
systems.
Resetting the Autonomic Nervous System, allowing the body to
finally re-enter its profound "Self-Healing Mode."
Kundalini Blood Treatment ( Chakra cleansing )

การนวด
มุ่งเน้น เทคนิคการถ่ายเทธาตุ เพื่อปรับสมดุล สู่ระบบต่อมไร้ท่อ
ลดอาการ ปวด บวม อักเสบ อุดกั้น ในหลอดเลือด โป่งพอง

การสื่อสารระหว่างลำใส้ และ สมอง Communication Between gut
and brain
You're talking about the fascinating world of the gut-brain axis! It's incredible how much we're learning about
the connection between our gut and our brain, and how much our gut health
influences our overall well-being.
What is the gut-brain axis?
It's a complex communication network that links your gut and
your brain, with a lot of back and forth between the two. Think of it like a
superhighway of information! Here's what's involved:
* The Vagus Nerve:
This is like the main telephone line between your brain and your gut. It sends
signals in both directions, letting your brain know what's happening in your
digestive system.
*
Neurotransmitters: Your gut produces
many of the same neurotransmitters as your brain, including serotonin (a mood
regulator), dopamine (involved in motivation and reward), and GABA (which has
calming effects).
* Hormones: Your gut releases hormones that can affect
your brain function, appetite, and even your stress response.
* The Immune
System: A huge part of your immune
system is in your gut! And the microbes
living there (your gut microbiota) have a big impact on your immune responses,
which can affect inflammation throughout your body, including your brain.
How does your gut affect your brain?
* Mood: Those gut microbes play a key role in producing
neurotransmitters that influence your mood, stress levels, and even anxiety. An
imbalance in your gut bacteria can affect how you feel.
* Brain
Function: A healthy gut is linked to
better cognitive function, including memory, focus, and learning.
* Behavior: Emerging research suggests that gut microbes
might even influence things like decision-making and social behavior.
Keeping your gut happy for a healthy brain:
* Eat a diverse
diet: Load up on fruits, vegetables,
whole grains, and prebiotics (which feed the good bacteria in your gut).
* Include
probiotics: Foods like yogurt, kimchi,
and sauerkraut contain beneficial bacteria that can support gut health.
* Manage stress: Chronic stress can wreak havoc on your gut.
Find healthy ways to manage stress, such as exercise, mindfulness, or spending
time in nature.
* Prioritize
sleep: Getting enough sleep is crucial
for both your gut and your brain to repair and rejuvenate.
The gut-brain axis is a hot area of research, and scientists
are still unraveling all the complexities. But one thing is clear: taking care
of your gut is a smart move for your overall health and well-being!

ควบคุมกล้ามเนื้อคอเพื่อส่งอาหารและอากาศไปตามท่อที่ถูกต้อง Controls throat muscles to send food and air down the right
tubes
You're talking about the fascinating world of the gut-brain
axis! It's incredible how much we're
learning about the connection between our gut and our brain, and how much our
gut health influences our overall well-being.
What is the gut-brain axis?
It's a complex communication network that links your gut and
your brain, with a lot of back and forth between the two. Think of it like a
superhighway of information! Here's what's involved:
* The Vagus Nerve:
This is like the main telephone line between your brain and your gut. It sends
signals in both directions, letting your brain know what's happening in your
digestive system.
*
Neurotransmitters: Your gut produces
many of the same neurotransmitters as your brain, including serotonin (a mood
regulator), dopamine (involved in motivation and reward), and GABA (which has
calming effects).
* Hormones: Your gut releases hormones that can affect
your brain function, appetite, and even your stress response.
* The Immune
System: A huge part of your immune
system is in your gut! And the microbes
living there (your gut microbiota) have a big impact on your immune responses,
which can affect inflammation throughout your body, including your brain.
How does your gut affect your brain?
* Mood: Those gut microbes play a key role in producing
neurotransmitters that influence your mood, stress levels, and even anxiety. An
imbalance in your gut bacteria can affect how you feel.
* Brain
Function: A healthy gut is linked to
better cognitive function, including memory, focus, and learning.
* Behavior: Emerging research suggests that gut microbes
might even influence things like decision-making and social behavior.
Keeping your gut happy for a healthy brain:
* Eat a diverse
diet: Load up on fruits, vegetables,
whole grains, and prebiotics (which feed the good bacteria in your gut).
* Include
probiotics: Foods like yogurt, kimchi,
and sauerkraut contain beneficial bacteria that can support gut health.
* Manage stress: Chronic stress can wreak havoc on your gut.
Find healthy ways to manage stress, such as exercise, mindfulness, or spending
time in nature.
* Prioritize
sleep: Getting enough sleep is crucial
for both your gut and your brain to repair and rejuvenate.
The gut-brain axis is a hot area of research, and scientists
are still unraveling all the complexities. But one thing is clear: taking care
of your gut is a smart move for your overall health and well-being!
มีหน้าที่รับผิดชอบ การเคลื่อนไหวของกล้ามเนื้อการพูด/เสียง Responsible for speech muscle movements/sound
The motor cortex is the part of the brain primarily responsible for the muscle
movements needed for speech production. It sends signals to the muscles in your
face, tongue, and throat, telling them how to move to form words and sounds.
However, speech production is a complex process that
involves several other important components:
* Respiratory System:
The lungs and diaphragm provide the air needed for speech.
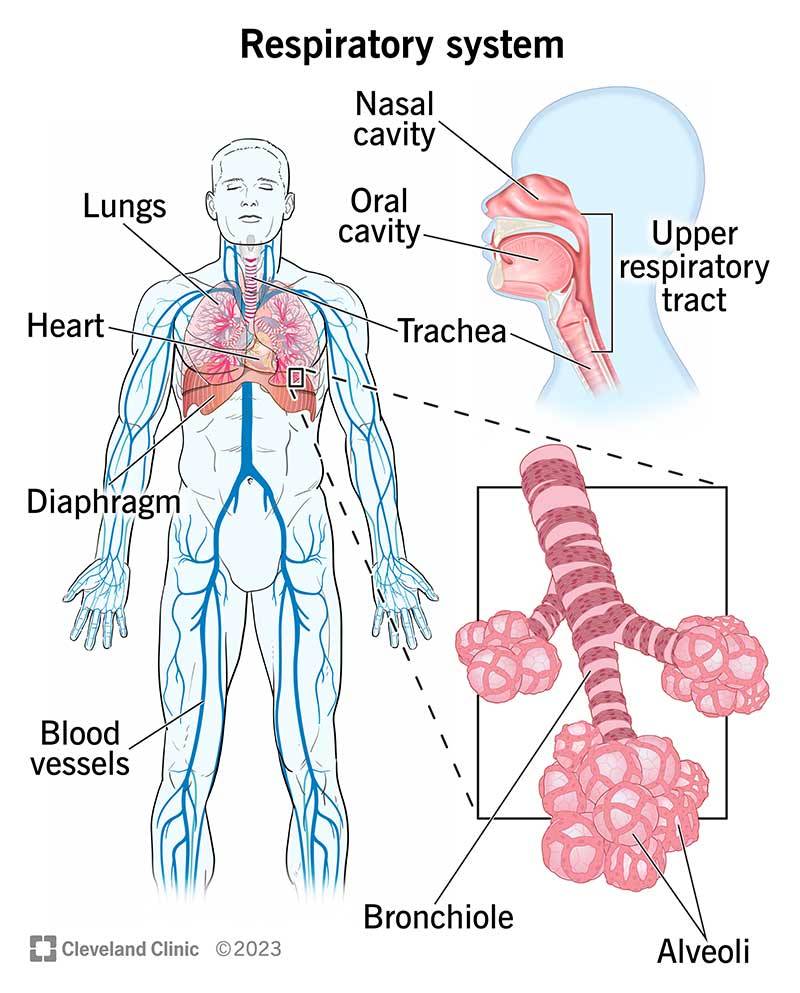
* Larynx (Voice Box):
Contains the vocal cords, which vibrate to produce sound when air passes
through them.
* Articulators: The
tongue, teeth, lips, and palate work together to shape the sounds produced by
the vocal cords into recognizable speech.
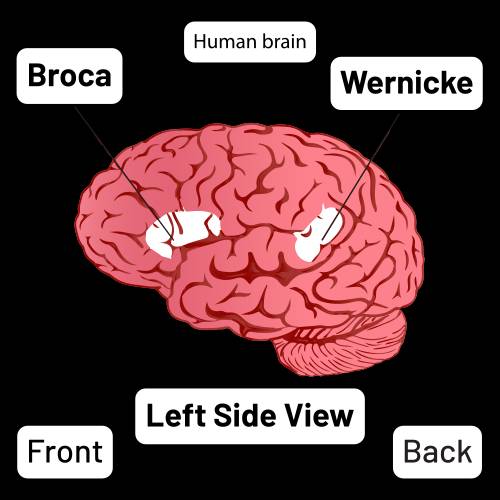
* Brain: In addition
to the motor cortex, other areas of the brain, such as Broca's area and
Wernicke's area, are crucial for language processing and comprehension.
Therefore, while the motor cortex is directly responsible
for the muscle movements, it's important to remember that speech production is
a result of the coordinated effort of all these components.
ลดความดันโลหิต/อัตราการเต้นของหัวใจในกรณีเจ็บป่วยหรือความเครียดทางอารมณ์
Lowers blood pressure/heart
rate in the case of illness or emotional
stress
It seems like you're describing the function of the parasympathetic nervous
system.
Here's why:
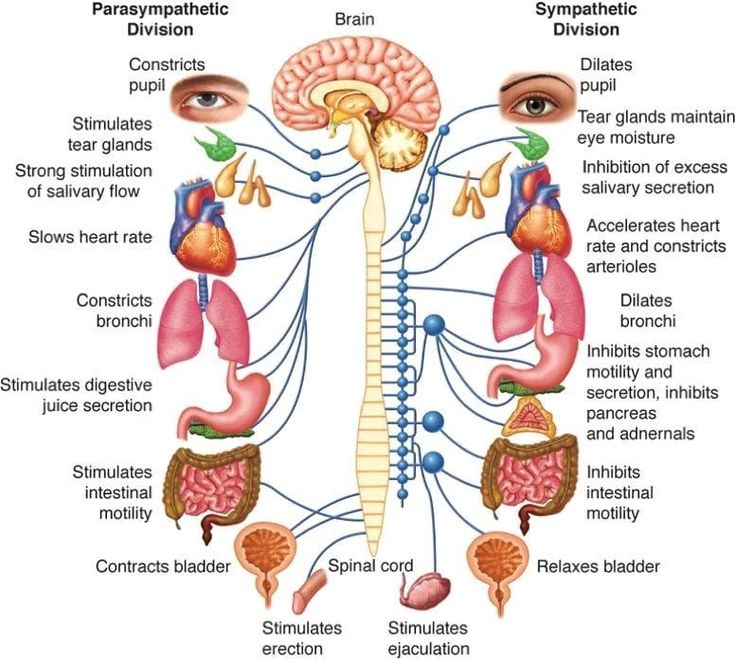
* Parasympathetic vs.
Sympathetic: Our nervous system has two
main branches: the sympathetic and the parasympathetic. The sympathetic nervous
system is responsible for the "fight-or-flight" response, increasing
heart rate and blood pressure when we face danger or stress. The
parasympathetic nervous system does the opposite – it promotes "rest and
digest" functions, slowing heart rate and lowering blood pressure.
* Maintaining
Balance: These two systems work together
to maintain balance in your body. When a stressful situation arises, the
sympathetic system kicks in. Afterward, the parasympathetic system helps you
calm down and return to a normal state.
In the case of illness or emotional stress:
* Illness: When
you're sick, your body needs to conserve energy for healing. The
parasympathetic system helps by lowering your heart rate and blood pressure.
* Emotional
Stress: While the sympathetic system
initially responds to stress, prolonged stress can be harmful. The parasympathetic system helps.
Important Note: If you're experiencing frequent or
concerning changes in your blood pressure or heart rate, it's crucial to
consult a medical professional for proper evaluation and guidance.

การผ่อนคลายกับการหายใจ. Relaxation with breathing
Relaxation with breathing is a powerful way to calm your mind and body. Here's
how you can do it:
1. Find a Comfortable Position:
* Sit or lie down in
a comfortable position.
* Ensure your spine
is straight, but not stiff.
* If sitting, keep
your feet flat on the floor.
* If lying down, rest
your arms by your side.
2. Focus on Your Breath:
* Close your eyes
gently.
* Bring your
attention to your natural breath, noticing the sensation of each inhale and
exhale.
* Observe the rise
and fall of your abdomen or chest.
3. Deepen Your Breathing:
* Gradually start to
deepen your breaths.
* Inhale slowly and
deeply through your nose, filling your lungs completely.
* Exhale slowly and
fully through your nose or mouth.
4. Techniques to Enhance Relaxation:
* Counting Breaths:
Count each breath, or count each cycle of inhalation and exhalation. This helps
to anchor your mind and prevent it from wandering.
* Equal Breathing:
Inhale for a specific count, and then exhale for the same count. For example,
inhale for a count of 4, and exhale for a count of 4.
* Progressive Muscle
Relaxation: Combine deep breathing with progressive muscle relaxation. Tense
and release different muscle groups in your body, starting with your toes and
moving up to your head.
5. Practice Regularly:
* Aim to practice
relaxation breathing for at least 10-15 minutes each day.
* You can practice
anytime, anywhere – when you wake up, before bed, or during a stressful
situation.
Benefits of Relaxation Breathing:
* Reduces stress and
anxiety
* Lowers blood
pressure
* Improves sleep
quality
* Increases focus and
concentration
* Promotes a sense of
well-being
Tips:
* If your mind
wanders, gently bring it back to your breath.
* Don't force your
breathing. Let it flow naturally.
* Create a peaceful
environment by minimizing distractions.
* You can also listen
to calming music or nature sounds while practicing.
With regular practice, relaxation breathing can become a
valuable tool for managing stress and improving your overall health and
well-being.
การทำงานของอวัยวะที่ดีต่อสุขภาพ - หัวใจ ตับ ปอด
ตับอ่อน ลำไส้ Healthy organ functioning
- heart, liver, lung, pancreas, intestines
It's great you're thinking about your health! Here's a breakdown of how to keep
your heart, liver, lungs, pancreas, and intestines functioning well:
Heart:
* Eat a heart-healthy
diet: Focus on fruits, vegetables, whole
grains, lean protein, and healthy fats (like those found in avocados and nuts).
Limit saturated and trans fats, cholesterol, sodium, and added sugars.
* Stay active: Aim
for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic activity or 75 minutes
of vigorous-intensity aerobic activity per week.
* Maintain a healthy
weight: Losing even a small amount of weight can make a big difference for your
heart health.
* Don't smoke:
Smoking is a major risk factor for heart disease.
* Manage stress: Find
healthy ways to cope with stress, such as exercise, relaxation techniques, or
spending time with loved ones.
* Control blood
pressure and cholesterol: Work with your
doctor to manage these important factors.
Liver:
* Limit alcohol
intake: Excessive alcohol consumption can damage your liver.
* Maintain a healthy
weight: Obesity can increase your risk of liver disease.
* Get
vaccinated: Talk to your doctor about
vaccinations for hepatitis A and B.
* Be cautious with
medications and supplements: Always
follow dosage instructions and talk to your doctor about potential
liver-related side effects.
* Avoid toxins: Limit
exposure to cleaning products and other chemicals that can harm your liver.
Lungs:
* Don't smoke:
Smoking is the leading cause of lung disease.
* Avoid secondhand
smoke and air pollution: These can also
damage your lungs.
* Get vaccinated: Get
vaccinated against the flu and pneumonia.
* Exercise regularly:
Exercise helps strengthen your lungs.
* Prevent infections:
Wash your hands frequently and avoid close contact with people who are sick.
Controls digestion and is responsible for your
"full" feeling
ควบคุมการย่อยอาหาร และรับผิดชอบต่อความรู้สึก
"เต็มที่" ของคุณ

Acts like a brake lever to the gas pedal of the sympathetic nervous
system (slows your ANS down)
ทำหน้าที่เหมือนคันโยกเบรกไปยังคันเร่งแก๊สของระบบประสาทซิมพาเทติก
(ทำให้ ANS ของคุณช้าลง)
Kundalini Blood Treatment for male reproductive system disorders (using hot
stone technique to awaken Kundalini for healing male reproductive system
disorders) กระษัยความเสื่อมโทรม

